There is no universal standard for DSCR; however, most lenders want to see at least a 1.25 or 1.50. We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. For example, if a company has a DSCR of 0.5, then it is able to cover only 50% of its total debt commitments. There can be an overlook of one-time or irregular expenses, potentially inflating the DSCR. Any ratio value at, or just above, 1 should therefore be viewed with caution, since the slightest reduction in earnings could cause a business to become financially overextended.
Great! Hit “Submit” and an Advisor Will Send You the Guide Shortly.
- Having an idea of your business’s ability to cover current debt can help you understand its ability to scale and plan strategically for growth.
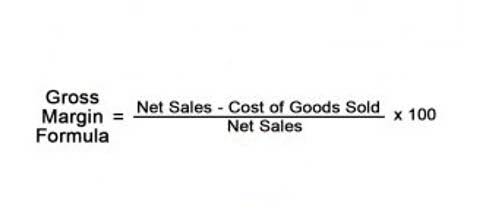
- The debt-service coverage ratio (DSCR) measures a firm’s available cash flow to pay current debt obligations.
- This ratio is particularly significant in the evaluation of long-term loans and business loans, ensuring that the company’s cash flow is sufficient for loan repayment.
- Consider joining a growing cadre of acquisition entrepreneurs by enrolling in Acquira’s Accelerator program.
- When you want to investigate the solvency of a company you’re considering as an investment, that company’s ability to support its debt payments becomes a crucial consideration.
- By eliminating these costly obligations, you free up cash flow, making it easier to cover remaining debt payments and improve your financial stability.
Because of the complexities of financial accounting and the unique circumstances of your business, some items may also be excluded as exceptions. A high DSCR could result from a combination of factors like increased revenue, decreased expenses, or both. It signifies strong operational efficiency and financial management, allowing the entity more freedom to invest, save, or withstand economic downturns. If a company’s revenue or expense estimates are overly optimistic, the DSCR may give a misleading impression of financial stability. It’s crucial to use conservative projections and test different scenarios to account for potential variations.
Negotiate Better Loan Terms

Your DSCR could determine whether a lender issues you financing, as well as the rates and terms you’ll get. A high DSCR ratio generally indicates a business that has enough cash flow to pay its debt obligations. For a lender, this means less risk of issuing financing as there’s a smaller chance the company will default. Business lenders use debt service coverage ratio when deciding to approve a business loan. The number helps them understand how much additional debt your business can afford to take on.
What is a good or bad debt service coverage ratio?
Assessing the ratio helps financial managers identify scenarios where operational income may fall short of covering debt obligations. Because the debt service ratio measures a company’s ability to sustain its current level of debt, the higher the ratio value is, the better its debt servicing position. When calculating DSCR, annual debt obligations refer to payments that are due within one year. These figures, referred to as short-term debt, can also be obtained from your balance sheet. In this example, the DSCR of 2 signifies that the business generates twice the income needed to fulfill its current debt obligations. It should be used in conjunction with other financial metrics, such as the Current Ratio or Quick Ratio, to gain a holistic understanding of a company’s financial health.
Using DSCR in Context
Showing improved financial performance or providing additional collateral can help in securing better terms. This means that Burton makes enough in operating profits to pay his current debt service costs and be left with 30 percent of his profits. The DSCR calculation may be adjusted to be based on net operating income, EBIT, or EBITDA (depending on the lender’s requirement). If operating income, EBIT, or EBITDA are used, the company’s income is potentially overstated because not all expenses are being considered. A DSCR of 1 or above means that the company has surplus operating income that can be used to service its debts.
What is a DSCR Loan?
The approach allows for implementing risk mitigation measures to safeguard the entity against economic challenges. Let’s consider the example of an organization generating an annual net operating income of ₹ 15 crore. On the other hand, its total debt service, including principal and interest payments, is ₹ 12 crore. The NOI represents the revenue generated by contra asset account an entity’s core operational activities. You can derive the figure by subtracting operating expenses, excluding interest and taxes, from the total revenue. A higher NOI indicates a more substantial capacity to cover debt service requirements.

- The interest coverage ratio (ICR) evaluates the capacity to cover interest payments.
- Generally, a DSCR of greater than 1 is favorable as it indicates that the entity has adequate income to cover its debts.
- Exclude non-recurring expenses from the calculation to provide a more accurate representation of the entity’s ongoing debt-servicing capacity.
- Lenders may consider a DSCR below one as a sign of financial risk, which can impact loan approval and terms.
The DSCR is used primarily by lenders to assess the financial viability of companies seeking loans. It indicates whether a company can cover its debt obligations using debt service coverage ratio its operating income. A high DSCR suggests that the company generates enough income to meet its debt payments, making it a lower risk for lenders.

For example, lenders relaxed their minimum DSCR score requirements in the years leading up to the financial crisis of 2008. As a result, borrowers with low debt ratio scores had easier access to funds. For example, they might reduce their amount of debt requested, or may reduce their expenses in order to increase their operating income and therefore their DSCR. Commonly used in lending decisions, especially for assessing creditworthiness in new projects or expansions. A higher DSCR can account for uncertainties and provide a safety margin for new projects.

Understanding how to interpret the Debt Service Coverage Ratio (DSCR) is essential for evaluating a company’s financial stability and creditworthiness. Different DSCR values can signify varying levels of risk and financial health, influencing decisions made by lenders, investors, and business owners. For example, if a company had Bookstime a ratio of 1, that would mean that the company’s net operating profits equals its debt service obligations. In other words, the company generates just enough revenues to pay for its debt servicing. A ratio of less than one means that the company doesn’t generate enough operating profits to pay its debt service and must use some of its savings.

